2023 World Press Freedom Index – journalism threatened by fake content industry
The 21st edition of the World Press Freedom Index, compiled annually by Reporters Without Borders (RSF), sheds light on major and often radical changes linked to political, social and technological upheavals.
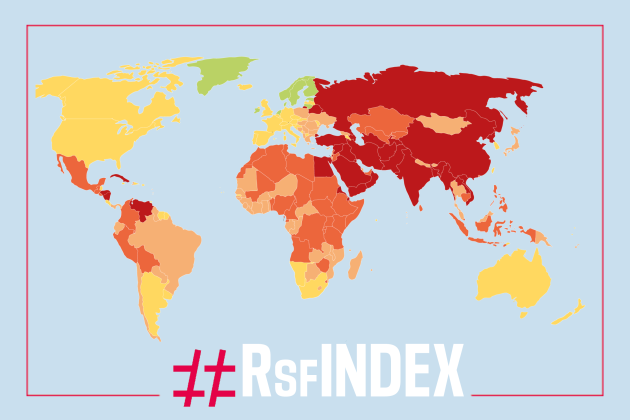
According to the 2023 World Press Freedom Index – which evaluates the environment for journalism in 180 countries and territories and is published on World Press Freedom Day (3 May) – the situation is “very serious” in 31 countries, “difficult” in 42, “problematic” in 55, and “good” or “satisfactory” in 52 countries. In other words, the environment for journalism is “bad” in seven out of ten countries, and satisfactory in only three out of ten.
Norway is ranked first for the seventh year running. But – unusually – a non-Nordic country is ranked second, namely Ireland (up 4 places at 2nd), ahead of Denmark (down 1 place at 3rd). The Netherlands (6th) has risen 22 places, recovering the position it had in 2021, before crime reporter Peter R. de Vries was murdered.
There are changes at the bottom of the Index, too. The last three places are occupied solely by Asian countries: Vietnam (178th), which has almost completed its hunt of independent reporters and commentators; China (down 4 at 179th), the world’s biggest jailer of journalists and one of the biggest exporters of propaganda content; and, to no great surprise, North Korea(180th).